
Student Projects
General Stair-climbing Robot
Project Video
Team Members
Team Members:
隽昕哲 Xinzhe Juan, 黄珏 Jue Huang, 陈昱希 Yuxi Chen, 周宇晟 Yusheng Zhou
Instructors:
Mian Li
Project Description
-
Problem
When we observe the common robots that we have around us, such as robot cleaner, delivering machine, detecting robot. We may find that most of their driving modes is wheels or caterpillar bands. [2] This type of moving mode makes it hard to perform longitudinal movement like climbing up stairs.
Nevertheless, circumstances still exists when there is only staircase available. If our house has more than one floor or even have several stairs in the corridor to the kitchen, the robot cleaner is unable to cover the whole area of your house. Also, during the period of quarantine in our university several months ago, using robot to deliver meals is the most efficient and safe way, given that most of our dormitory lack elevators, the robot delivers must possess the ability of climbing stairs. If we need to design a robot that can detect a building’s safety index after a fire or earthquake, the elevator is definitely unusable. The robot needs to climb dozens of stairs in the building’s escapeway in order to fully assess the building’s safety index.
To solve the puzzle, some stair-climbing robots have been developed. However, many of them have three common problems as listed below.
1. The models are space-consuming which cannot be used in our house.
2. The structure is too complicated for mass-producing.
3. The robots are unable to keep stable when climbing stairs.
-
Concept Generation
Given that the problem we have, our aim is to develop a new type of model forstair-climbing robot that can solve the problems mentioned above. Therefore,the concept of General Stair-climbing Robot is proposed corresponding to thethree aspects of demand.
First of all,the stair-climbing robot need to be flexible in narrow places like in ourbedroom or kitchen. The common wheel structure for civil robots today is thehidden small wheels under the machine. Taking the robot cleaner as an example,its wheels are half-embedded into their body part, which prevent the wheel fromgetting stuck by other object like strings. Hence, instead of relying onspecial wheels, mechanical structures will be constructed to realize the stair-climbingfunction.
Moreover, aconcise structure is needed for civil robots’ mass-producing. Acomplicated structure means there are more physical calculation for the parts,thus lead to the demand for preciseness of the parts. Also, the cost ofproducing the robot could be very high and it cannot be put intomass-producing. Therefore, we need the stair-climbing robot to have concisestructure.
Last but notleast, the robot should have a horizonal platform that remain stable when themodel is climbing stairs. If we need the robot to deliver dishes in arestaurant or detect the ground surface of stairs’levelness. The model must bestable all the way upstairs. In conclusion, the model should have at least onestable horizonal platform in any time.
-
Design Description
Our Stair-climbing Robot is generally composed of three parts, namely,the front part, the middle part and the back part, as is shown in figure 4. Each part can move up and down separately.
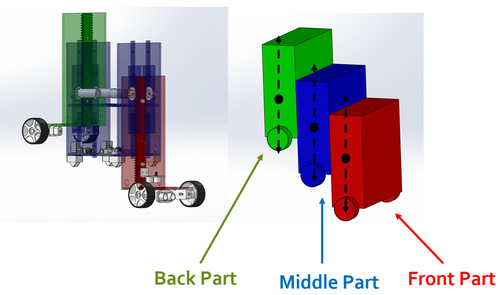
Figure1: The outlook of the Stair-climbing Robot(Generated by SOLIDWORKS 2019)
Two ultrasonic sensors are utilized in the front section of thetrolley to detect the stairs and capture the characteristics of the them. When the sensors detect that there is a stair in front of the trolley, the front partwill rise till it reaches the height of the stair. The time consumed for elevating the front part will be recorded and the middle as well as the back part will go up in accordance with it.
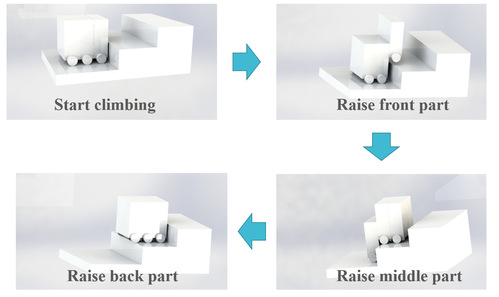
Figure2: The process of stair climbing(Generated by SOLIDWORKS 2019)
A specially designed lifting system is applied to make sure each part can rise and descend accordingly.We exert gear motors with gears and racks achieve this function. The racks areassembled in the front and back part of the trolley. We apply bolts to fix therack and board. Four gear motors are set in the middle part with gears. Two sets of boards are placed to connect the two parts of the car and guarantee thatonly up and down motion is available.
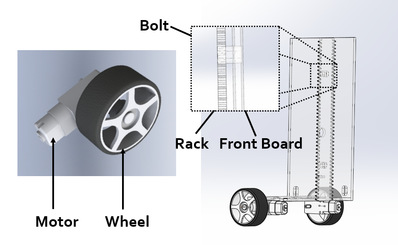
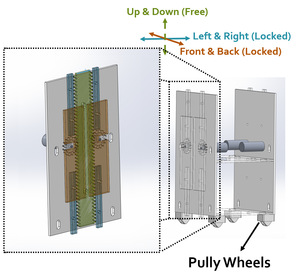
Figure3: The structure of front/back part Figure4: The structure of middle part
(Generated by SOLIDWORKS 2019) (Generated by SOLIDWORKS 2019)
-
Validation
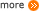
After finishing the assemble of our model, we determined its validation through the testing. We designed a special model of stairs that has two different heights in two direction. This testing stairs enabled us to explore its capability on whether the robot can go up or down staircase with different sizes. Thus, we could further improve the robot’s function.
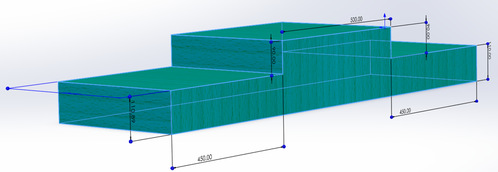
Figure 9: The simulated diagram of the stairs
-
Modeling and Analysis
The way to realize our project is mainly divided into three steps. Firstly,we designed structural parts of our robot through Solidworks software,and we use laser-cutting machine to curve the PMMA board into the shape we want. The next step is to assemble different parts together. Theoverall control system and essential lifting part of the robot are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Finally, The system is programmed in Arduino IDE software. And more tests are required to debug deviation between hardware and software.

Figure 6: Overall sysytem control diagram
-
Conclusion
The project solves the problem by designing a basic model acquiring stair-climbing function. Through specially designed structure, the model is able to climb stairs indifferent heights. We believe that in the future, the model can be adapted to civil robots in different situations that require its stair-climbing function
-
Acknowledgement
This project is supported by SJTU JI VG100 Section 1.
We are sincerely grateful to all those who have helped us in this project:
Professor: [Prof. Mian Li, Pro. Yang Liu, and Prof. Irene Wei]
Teaching Assistant: [Zijie Chen, Xiwen Cao and Jiaxuan Xu]
Lab Consultant: [Xinyu Wu]
More project information, please contact: [1akaman@sjtu.edu.cn]
-
Reference
[1] Takaki T, Aoyama T, Ishii I. Development ofinverted pendulum robot capable ofclimbing stairs using planetary wheel mechanism, 2013[C]. IEEE, 2013
[2] V. K, A. M, C. S, et al. Ascento: ATwo-Wheeled Jumping Robot: 2019 International Conference on Robotics andAutomation (ICRA), 2019[C].2019